Looking for a muse? Check no further. Discover the Best of Art, Culture, History & Beyond!

Throughout history, artists have produced art in a variety of media and styles following different philosophies and ideals. Although labelling may often result in being reductive, different artistic tendencies or styles can be grouped in collective titles known as art movements.
If speaking art seems like a discipline in itself to you, here we provide you with the top terms of art movements and styles, from Classicism to Futurism, from Baroque to Avant-garde.
Art History Timeline
| Art Period | Timeframe |
|---|---|
| Prehistoric Art | 40,000 BCE – 3000 BCE |
| Ancient Egyptian Art | 3000 BCE – 100 BCE |
| Mesopotamian Art | 3100 BCE – 539 BCE |
| Greek Art | 900 BCE – 31 BCE |
| Roman Art | 500 BCE – 476 CE |
| Byzantine Art | 330 CE – 1453 CE |
| Medieval Art | 500 CE – 1400 CE |
| Gothic Art | 1100 CE – 1500 CE |
| Renaissance | 1400 CE – 1600 CE |
| Baroque | 1600 CE – 1750 CE |
| Rococo | 1720 CE – 1780 CE |
| Neoclassicism | 1750 CE – 1830 CE |
| Romanticism | 1800 CE – 1850 CE |
| Realism | 1840 CE – 1880 CE |
| Impressionism | 1860 CE – 1890 CE |
| Post-Impressionism | 1885 CE – 1910 CE |
| Symbolism | 1880 CE – 1910 CE |
| Art Nouveau | 1890 CE – 1910 CE |
| Fauvism | 1905 CE – 1910 CE |
| Expressionism | 1905 CE – 1930 CE |
| Cubism | 1907 CE – 1914 CE |
| Futurism | 1909 CE – 1944 CE |
| Dada | 1916 CE – 1924 CE |
| Surrealism | 1924 CE – 1966 CE |
| Constructivism | 1913 CE – 1940 CE |
| Bauhaus | 1919 CE – 1933 CE |
| Abstract Expressionism | 1940 CE – 1950 CE |
| Color Field Painting | 1940 CE – 1970 CE |
| Minimalism | 1960 CE – Present |
| Pop Art | 1950 CE – 1970 CE |
| Op Art | 1955 CE – 1975 CE |
| Conceptual Art | 1960 CE – Present |
| Land Art | 1960 CE – Present |
| Postmodernism | 1970 CE – Present |
| Street Art | 1970 CE – Present |
| Digital Art | 1980 CE – Present |
Some of the Art Movements and Styles explained
(The list is being updated. Stay tuned! 😉 )
Abstract Expressionism
The designation ‘Abstract Expressionism’ encompasses a wide variety of American 20th-century art movements in abstract art. Also known as The New York School, this movement includes large painted canvases, sculptures and other media as well. The term ‘action painting’ is associated with Abstract Expressionism, describing a highly dynamic and spontaneous application of vigorous brushstrokes and the effects of dripping and spilling paint onto the canvas.
Read more about Abstract Expressionism.

Art Deco
Emerging in France before the First World War, Art Deco exploded in 1925 on the occasion of the Exposition des Arts Décoratifs (Exhibition of Decorative Arts). Blurring the line between different mediums and fields, from architecture and furniture to clothing and jewelry, Art Deco merged modern aesthetic with skillful craftsmanship, advanced technology, and elegant materials.

Art Nouveau
A decorative style that flourished between 1890 and 1910 throughout Europe and the U.S. Art Nouveau, also called Jugendstil (Germany) and Sezessionstil (Austria), is characterized by sinuous, asymmetrical lines based on organic forms. Although it influenced painting and sculpture, its chief manifestations were in architecture and the decorative and graphic arts, aiming to create a new style, free of the imitative historicism that dominated much of 19th-century art movements and design.
Avant-garde
In French, avant-garde means “advanced guard” and refers to innovative or experimental concepts, works or the group or people producing them, particularly in the realms of culture, politics, and the arts.
Baroque
The term Baroque, derived from the Portuguese ‘barocco’ meaning ‘irregular pearl or stone’, is a movement in art and architecture developed in Europe from the early seventeenth to mid-eighteenth century. Baroque emphasizes dramatic, exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted, detail, which is a far cry from Surrealism, to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur.

Rococo
Rococo is a movement in art, particularly in architecture and decorative art, that originated in France in the early 1700s. Rococo art characteristics consist of elaborate ornamentation and a light, sensuous style, including scrollwork, foliage, and animal forms.

Bauhaus
The school of art and design was founded in Germany by Walter Gropius in 1919 and shut down by the Nazis in 1933. The faculty brought together artists, architects, and designers, and developed an experimental pedagogy that focused on materials and functions rather than traditional art school methodologies. In its successive incarnations in Weimar, Dessau, and Berlin, it became the site of influential conversations about the role of modern art and design in society.

Neoclassicism
Almost the opposite of pop art in terms of inspiration, this style is one that arose in the second half of the eighteenth century in Europe, drawing inspiration from the classical art and culture of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome, which is not uncommon for art movements.
CoBrA
Founded in 1948 in Paris, CoBrA was a short-lived yet ground-breaking post-war group gathering international artists who advocated spontaneity as a means to create a new society. The name ‘CoBrA’ is an acronym for the home cities of its founders, respectively Copenhagen, Brussels and Amsterdam.
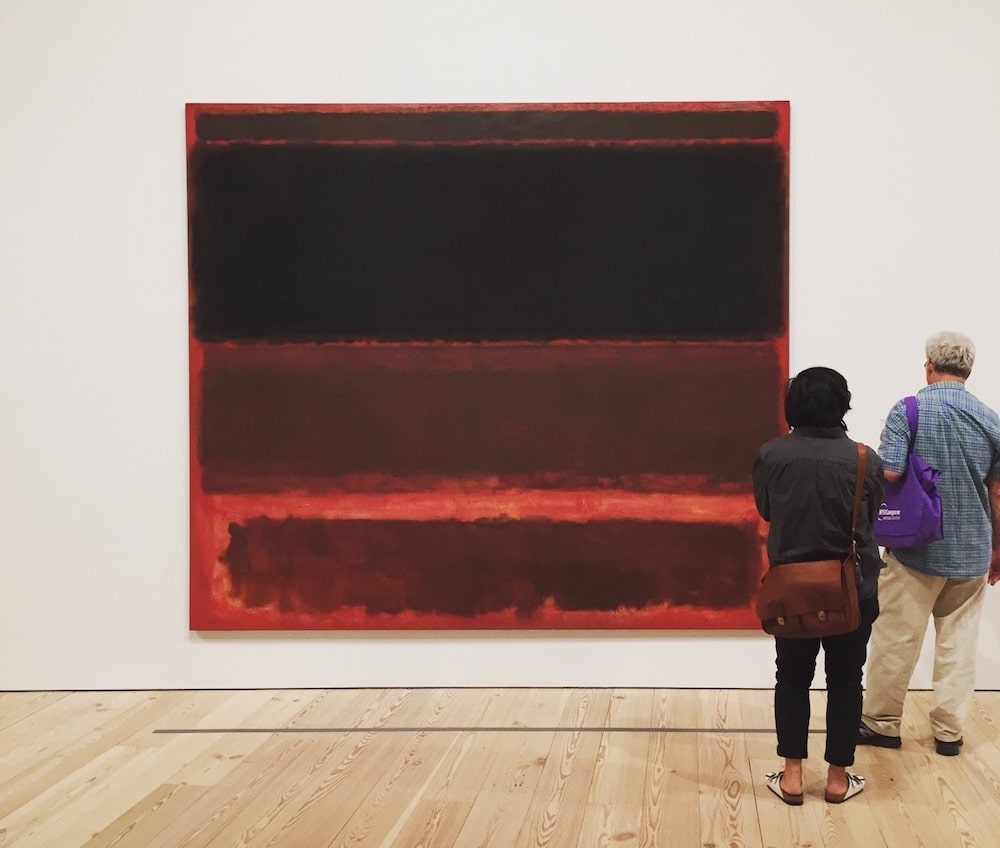
Color Field Painting
Often associated with Abstract Expressionism, the Colour Field painters were concerned with the use of pure abstraction but rejected the active gestures typical of Action Painting in favor of expressing the sublime through large and flat surfaces of contemplative colour and open compositions.
Read more about Color Field Painting.
Conceptual art
Conceptual art, sometimes simply called conceptualism, was one of several 20th-century art movements that arose during the 1960s, emphasizing ideas and theoretical practices rather than the creation of visual forms. The term was coined in 1967 by the artist Sol LeWitt, who gave the new genre its name in his essay “Paragraphs on Conceptual Art,” in which he wrote, “The idea itself, even if not made visual, is as much a work of art as any finished product.”
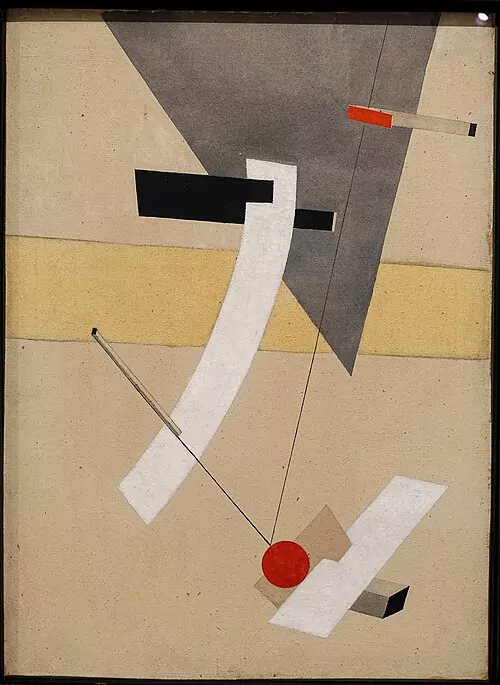
Constructivism
Developed by the Russian avant-garde around 1915, constructivism is a branch of abstract art, rejecting the idea of “art for art’s sake” in favour of art as a practice directed towards social purposes. The movement’s work was mostly geometric and accurately composed, sometimes through mathematics and measuring tools.
Cubism
An artistic movement began in 1907 by artists Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque who developed a visual language whose geometric planes challenged the conventions of representation in different types of art, by reinventing traditional subjects such as nudes, landscapes, and still lifes as increasingly fragmented compositions.
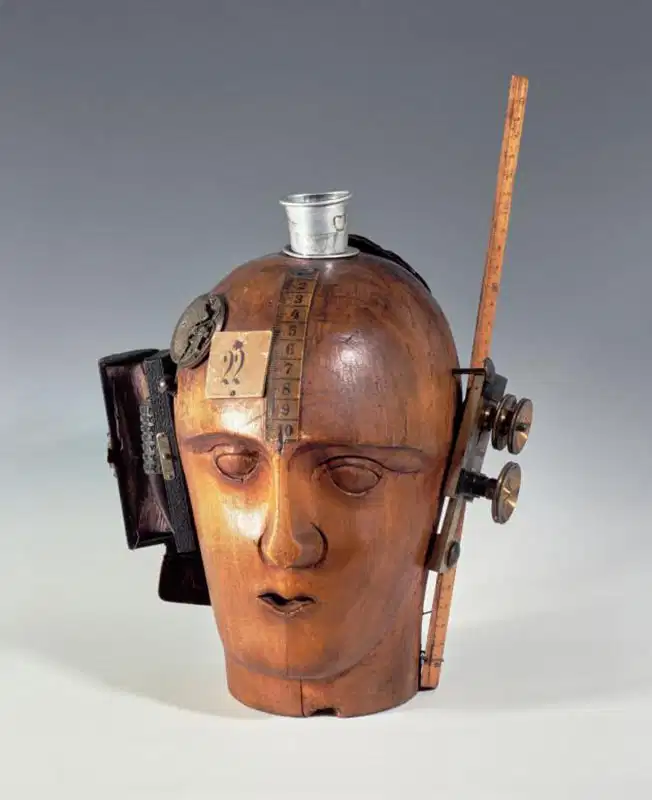

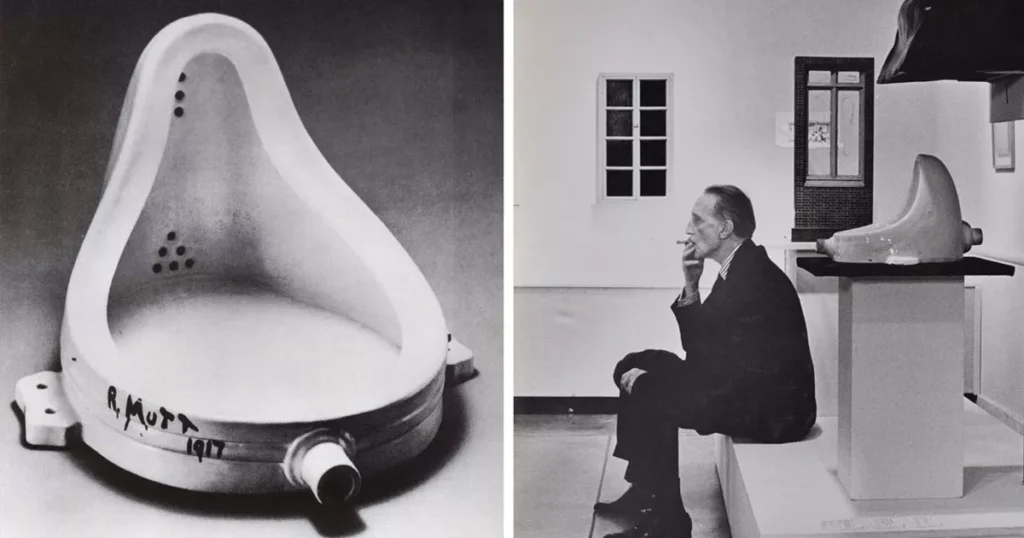
Dada / Dadaism
An artistic and literary movement in art formed during the First World War as a negative response to the traditional social values and conventional artistic practices of the different types of art at the time. Dada artists represented a protest movement with an anti-establishment manifesto, sought to expose accepted and often repressive conventions of order and logic by shocking people into self-awareness.
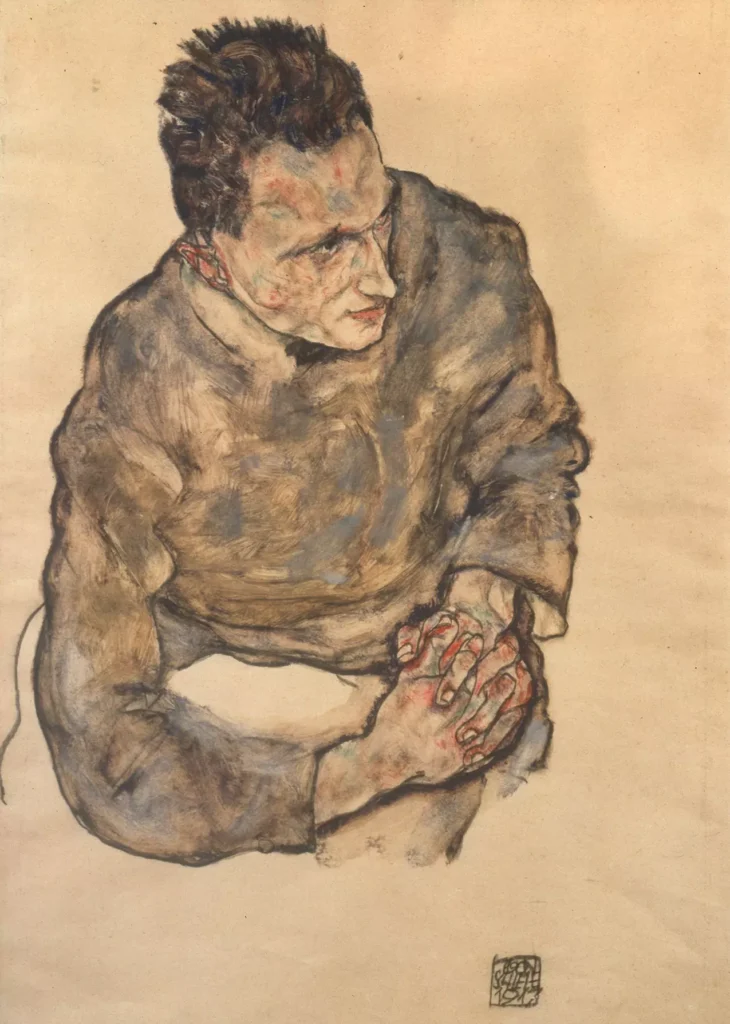

Expressionism
Expressionism is an international artistic movement in art, architecture, literature, and performance that flourished between 1905 and 1920, especially in Germany and Austria, that sought to express the meaning of emotional experience rather than physical reality. Conventions of the expressionist style include distortion, exaggeration, fantasy, and vivid, jarring, violent, or dynamic application of color in order to express the artist’s inner feelings or ideas.

Fauvism
Coined by the critic Louis Vauxcelles, Fauvism (French for “wild beasts”) is one of the early 20th-century art movements. Fauvism is associated especially with Henri Matisse and André Derain, whose works are characterized by strong, vibrant colour and bold brushstrokes over realistic or representational qualities.

Futurism
Fairly unique among different types of art movements, it is an Italian development in abstract art and literature, founded in 1909 by Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, aiming to capture the dynamism, speed and energy of the modern mechanical world.
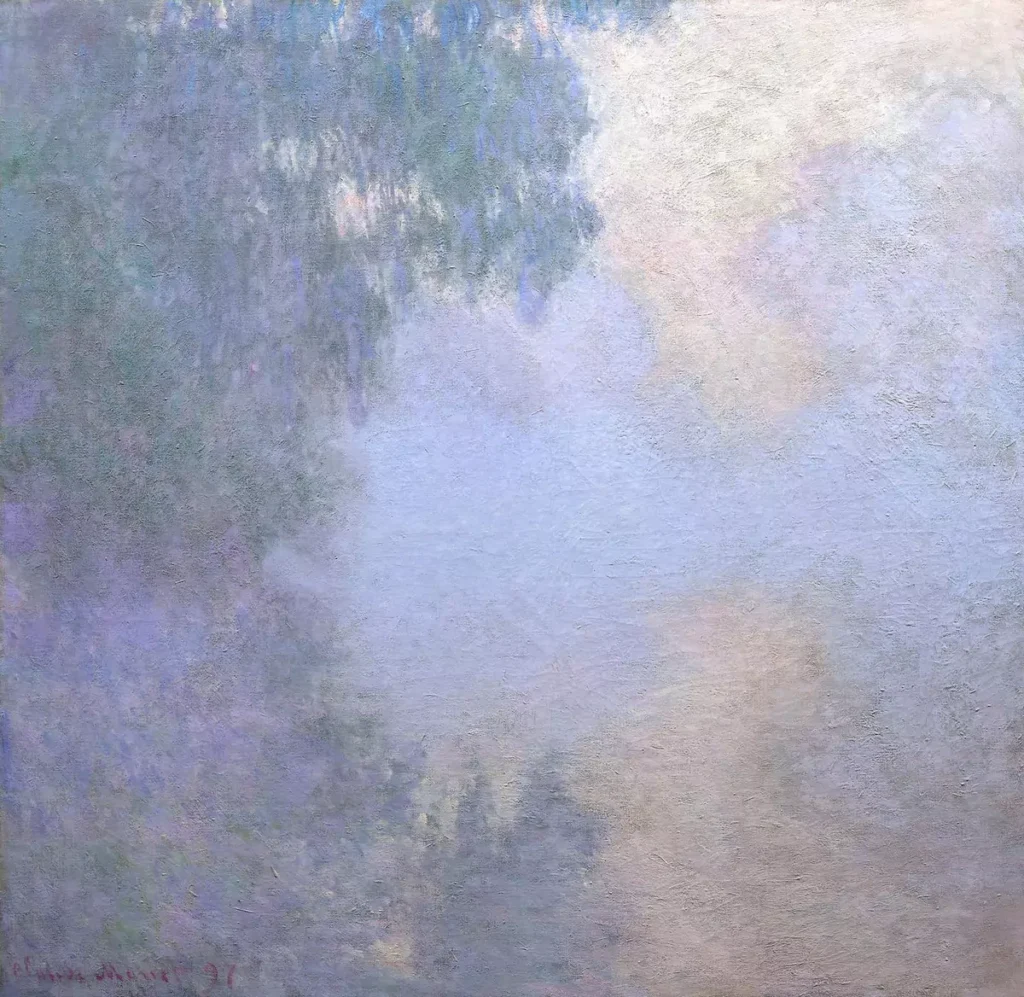

Impressionism
Impressionism is a 19th-century art movement, associated especially with French artists such as Claude Monet, Pierre Auguste Renoir, Camille Pissarro and Alfred Sisley, who attempted to accurately and objectively record visual ‘impressions’ by using small, thin, visible brushstrokes that coalesce to form a single scene and emphasize movement and the changing qualities of light.
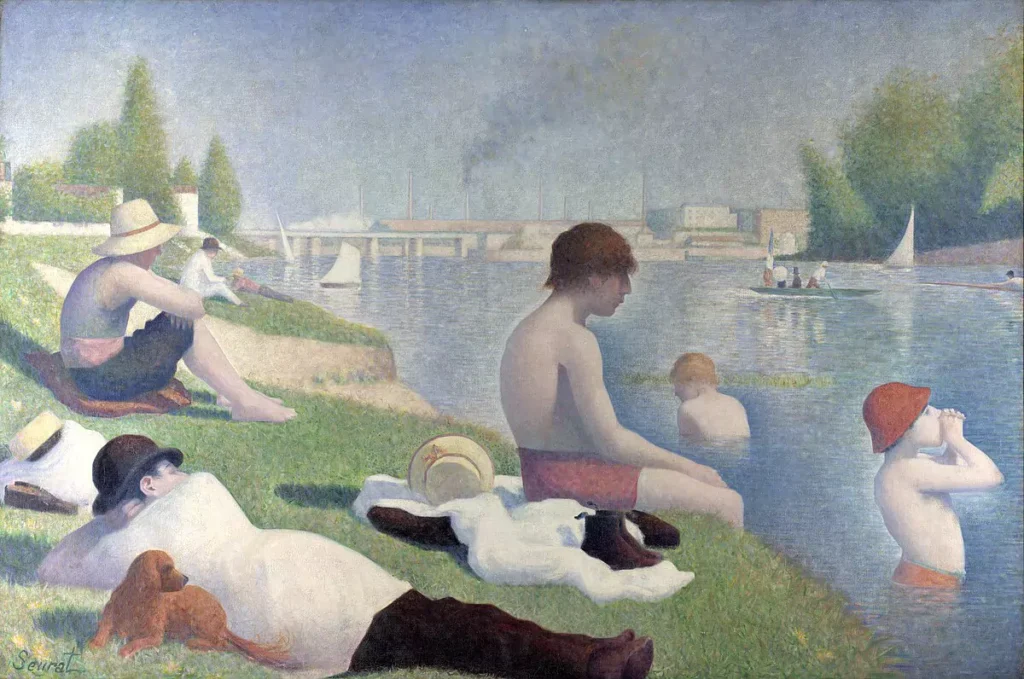
Neo-Impressionism
A term applied to an avant-garde art movement that flourished principally in France from 1886 to 1906. Led by the example of Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, Neo-Impressionists renounced the spontaneity of Impressionism in favour of a measured and systematic painting technique known as pointillism, grounded in science and the study of optics.
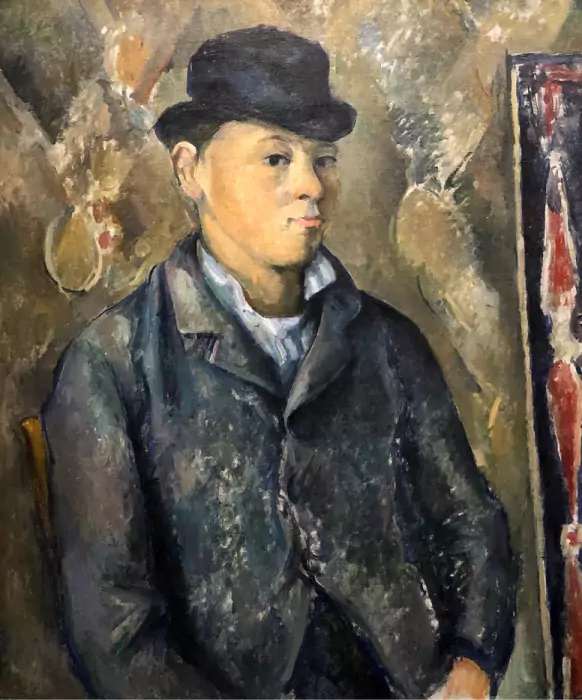
Post-Impressionism
Coined in 1910, the term ‘Post-Impressionism’ describes the reaction against the Impressionists’ naturalistic depiction of light and colour. Artists like Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, and Vincent van Gogh developed personal styles unified by their interest in expressing their emotional and psychological responses to the world through bold colours and often symbolic images.
Installation Art
Installation art is a movement developed at the same time as pop art in the late 1950s, which is characterized by large-scale, mixed-media constructions, often designed for a specific place or for a temporary period of time. Often, installation art involves the creation of an enveloping aesthetic or sensory experience in a particular environment, often inviting active engagement or immersion by the spectator.
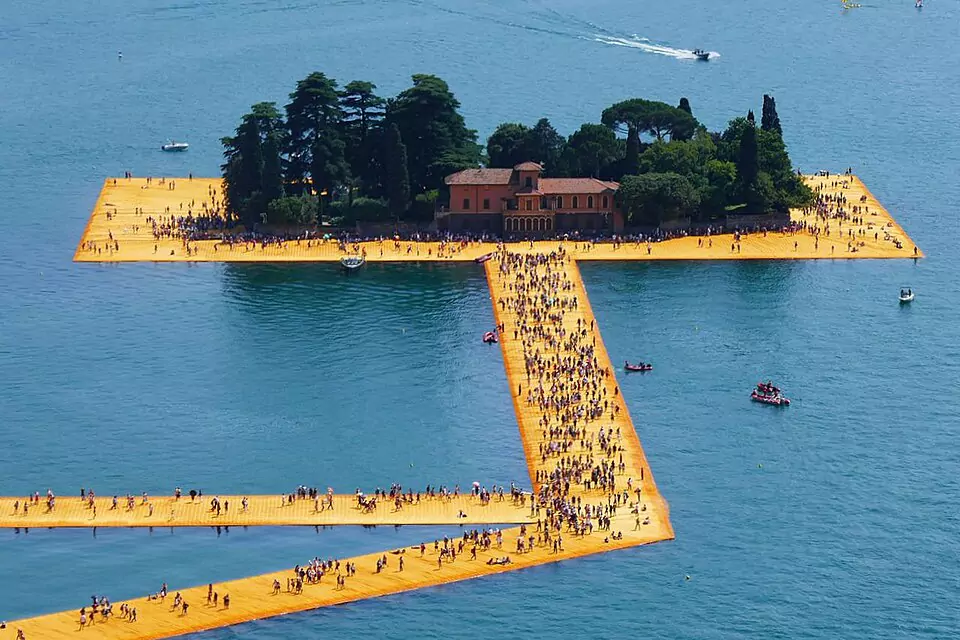

Land Art
Land art, also known as Earth art, Environmental art and Earthworks, is a simple art movement that emerged in the 1960s and 1970s, characterized by works made directly in the landscape, sculpting the land itself into earthworks or making structures in the landscape using natural materials such as rocks or twigs. It could be seen as a natural version of installation art. Land art is largely associated with Great Britain and the United States but includes examples from many countries.
Minimalism
Another one of the art movements from the 1960s, and typified by works composed of simple art, such as geometric shapes devoid of representational content. The minimal vocabulary of forms made from humble industrial materials challenged traditional notions of craftsmanship, the illusion of spatial depth in painting, and the idea that a work of abstract art must be one of a kind.
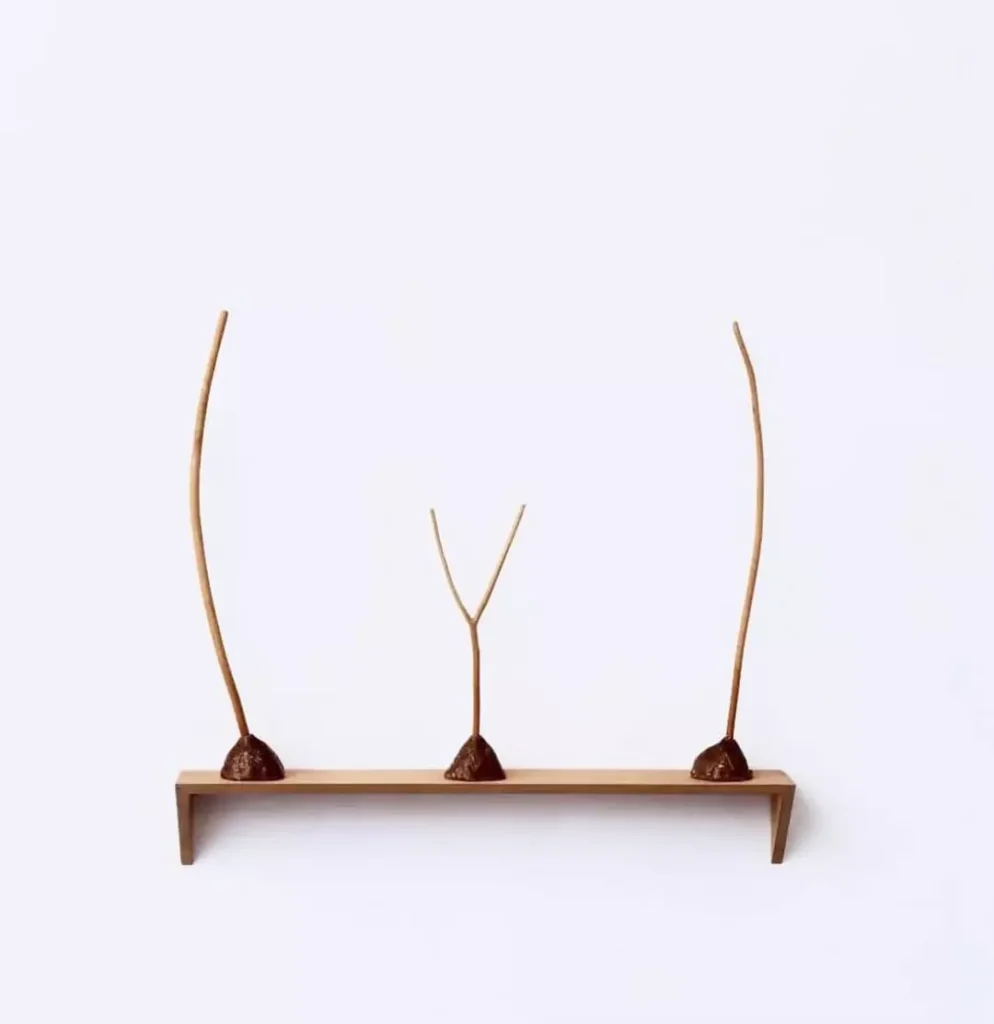

Op Art
Op Art is an abbreviation of optical art, a form of geometric abstract art that explores optical sensations through the use of visual effects such as repetition of simple forms, vibrating colour-combinations, moiré patterns, foreground-background confusion, and an exaggerated sense of depth. Op Art paintings and works employ tricks of visual perception like manipulating rules of perspective to give the illusion of three-dimensional space.
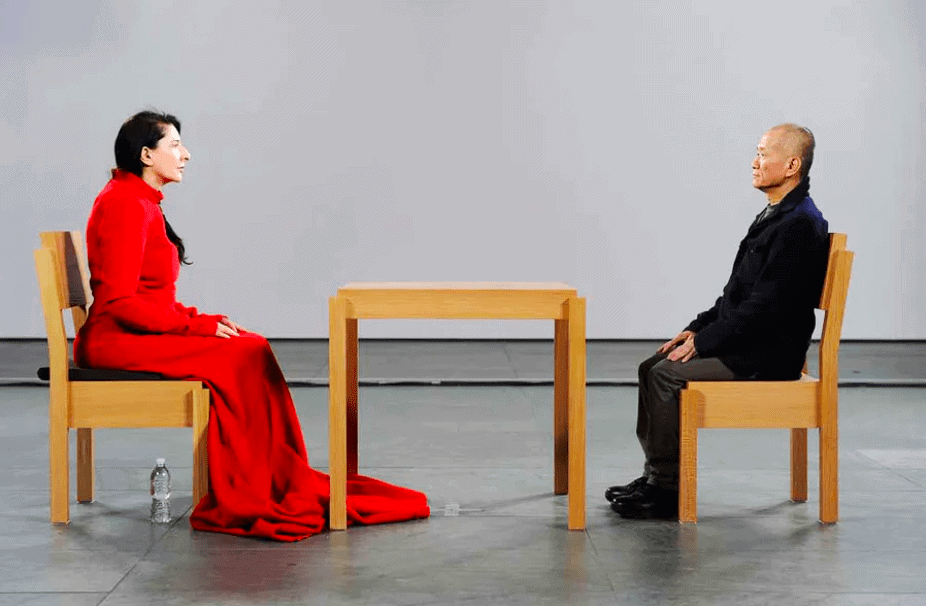

Performance Art
A term that emerged in the 1960s to describe different types of art that are created through actions performed by the artist or other participants, which may be live or recorded, spontaneous or scripted. Performance challenges the conventions of traditional forms of visual art such as painting and sculpture by embracing a variety of styles such as happenings, body art, actions, and events.
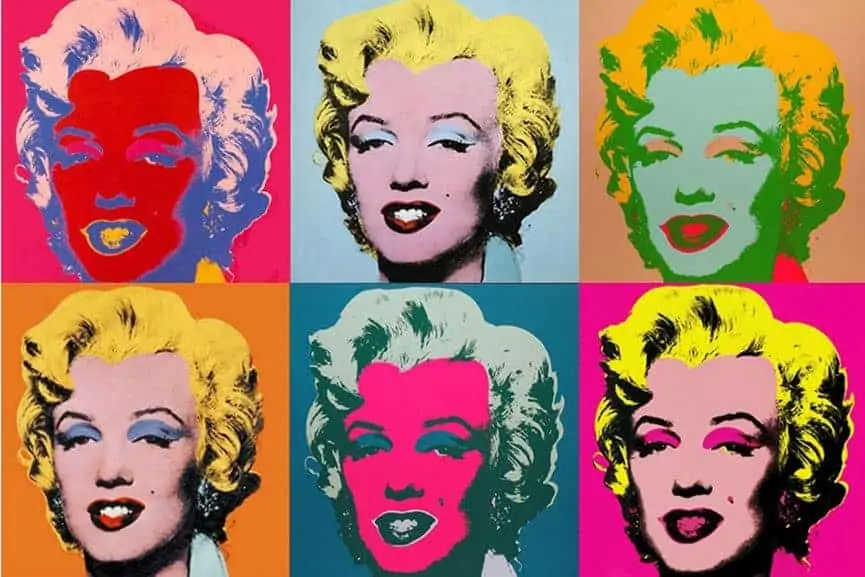

Pop Art
Pop Art emerged in the 1950s and was composed of British and American artists who draw inspiration from ‘popular’ imagery and products from commercial culture as opposed to ‘elitist’ fine art. Pop art reached its peak of activity in the 1960s, emphasizing the banal or kitschy elements of everyday life in such forms as mechanically reproduced silkscreens, large-scale facsimiles, and soft pop art sculptures.

Precisionism
Precisionism was the first real indigenous modern art movement in the United States and contributed to the rise of American Modernism. Taking its cues from Cubism and Futurism, Precisionism was driven by a desire to bring structure back to art and celebrated the new American landscape of skyscrapers, bridges and factories.
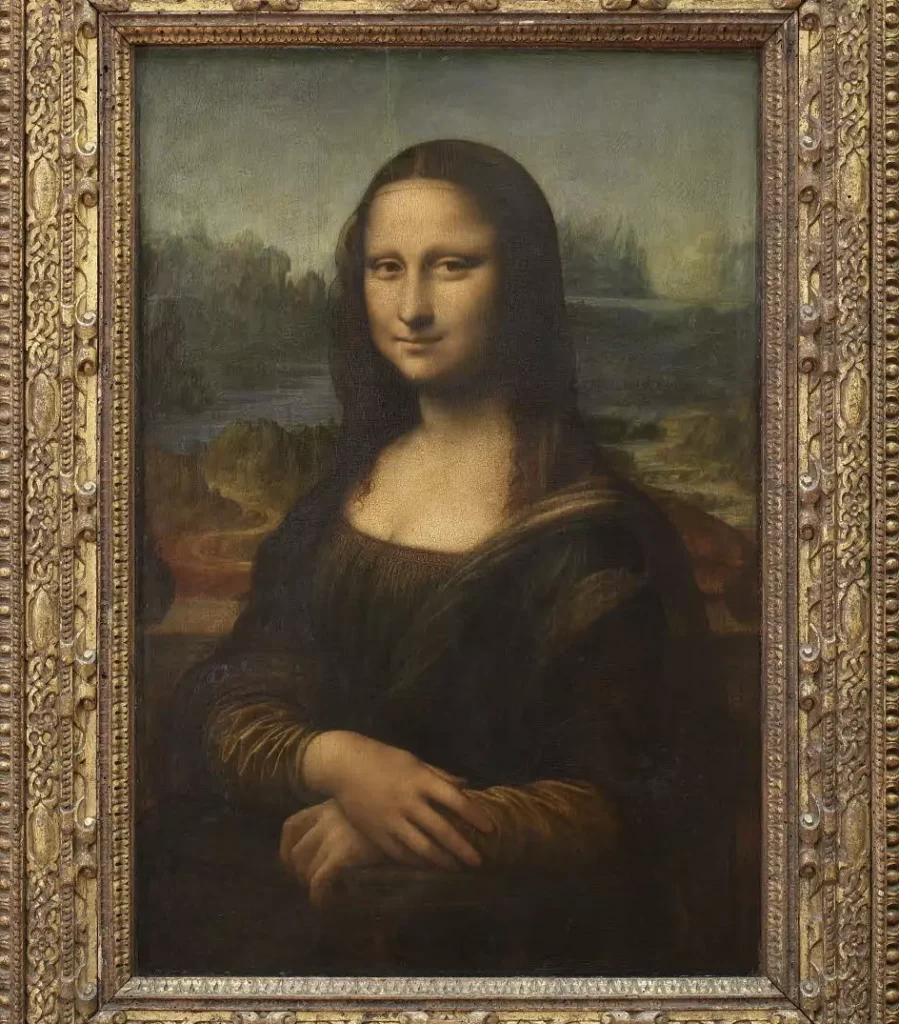

Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance wasn’t just a chapter in history—it was a rebirth, an explosion of creativity that reshaped the world forever. Emerging from the shadows of the Middle Ages, Italy in the 14th to 17th centuries became a powerhouse of intellect, artistry, and innovation. It was a time when the past met the future, when ancient wisdom blended with fresh perspectives, birthing a golden age that still captivates us today.
Surrealism
Founded by the poet André Breton in Paris in 1924, Surrealism was an artistic and literary movement that was active through World War II. The main goal of Surrealism painting and Surrealism artworks was to liberate thought, language, and human experience from the oppressive boundaries of rationalism by championing the irrational, the poetic and the revolutionary.

Suprematism
Found to be a relatively unknown member of the different types of abstract art movements, outside of the art world that is. A term coined by Russian artist Kazimir Malevich in 1915 to describe an abstract style of painting that conforms to his belief that art expressed in the simplest geometric forms and dynamic compositions was superior to earlier forms of representational art, leading to the “supremacy of pure feeling or perception in the pictorial arts.”

Symbolism
Symbolism emerged in the second half of the 19th century, mainly in Catholic European countries where industrialisation had developed to a great degree. Starting as a literary movement, Symbolism was soon identified with a young generation of painters who wanted art to reflect emotions and ideas rather than to represent the natural world in an objective way, united by a shared pessimism and weariness of the decadence in modern society.

Zero Group
Emerged in Germany and spread to other countries in the 1950s, Zero Group was a group of artists united by the desire to move away from the subjectivity of post-war movements, focusing instead on the materiality, color, vibration, light, and movement of pure abstract art. The main protagonists of the group were Heinz Mack, Otto Piene, and Günther Uecker.
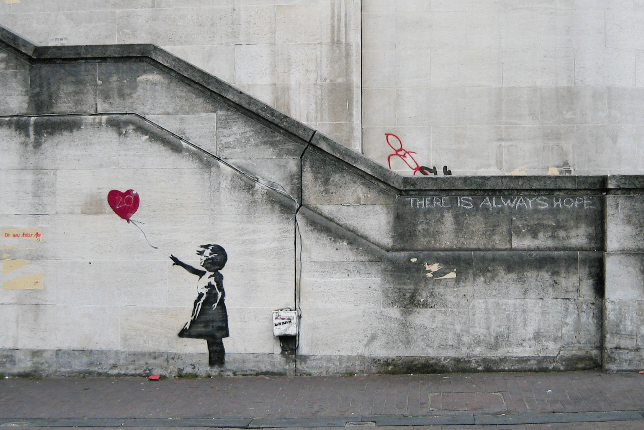

Street Art
Evolving from early forms of graffiti, Street Art is a thought-provoking art movement that emerged in the 1960s and peaked with the spray-painted New York subway train murals of the 1980s. Street artists use urban spaces as their canvas, turning cities around the globe into open sky museums and have often found their way into the mainstream art world.

Neon Art
In the 1960s, Neon Art turned a commercial medium employed for advertising into an innovative artistic medium. Neon lighting allowed artists to explore the relationship between light, colour, and space while tapping into pop culture imagery and consumerism mechanisms.
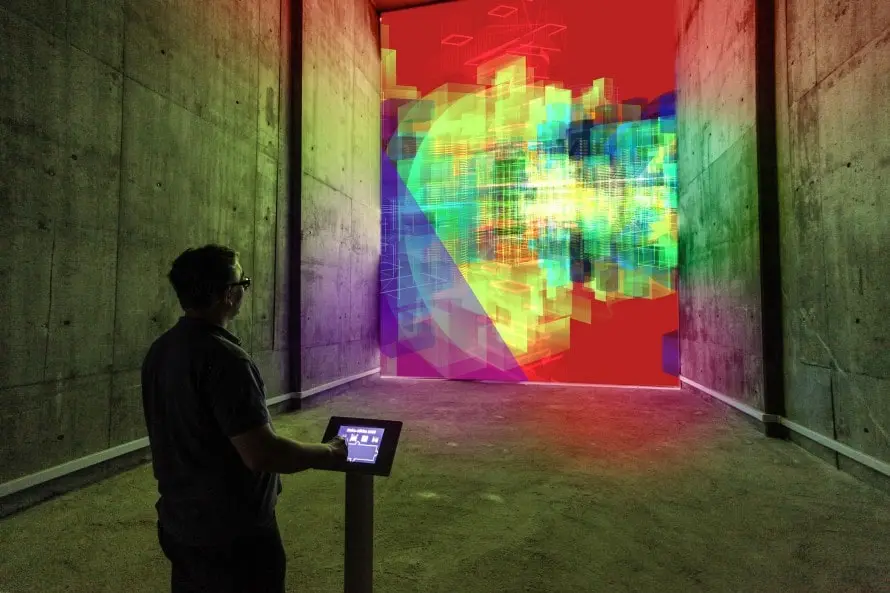

Digital Art
Digital Art broadly covers a variety of creative practices that employ different electronic technologies and result in a final product that is also digital. From computer graphics to virtual reality, from artificial Intelligence to NFT technology, the Digital Art spectrum is wide, innovative, and under the spotlight of the contemporary art market.
Learn more art terminology with:
MoMA – Glossary of Art Terms
Tate – Art Terms

This article is published on ArtAddict Galleria, where we explore the intersections of art, history, and culture. Stay tuned for more insights and discoveries!